NDCs Tracker
Fast Facts
- Behavioral risk factors to noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) include tobacco use and secondhand smoke, unhealthy diets such as excessive consumption of sugar, sodium, and fats; alcohol intake; and physical inactivity.
- Metabolic risk factors to NCDs include hypertension, overweight/obesity; high blood sugar levels, and high cholesterol.
- Environmental risk factors include indoor and outdoor air pollution.
- 80% of NCDs are preventable by modifying behavioral risk factors and making healthier lifestyle choices.
- NCDs are the cause of 74% of deaths worldwide and 68% of deaths nationwide, making it the #1 cause of mortality and morbidity in the Philippines and globally.
- NCDs lead to a 24.5% increased risk of Filipinos dying prematurely between the ages 30 to 70 years old.
In 2018, the United Nations High-Level Meeting on NCDs introduced the 5x5 approach in its global response to the top five diseases that contribute the largest to the burden of NCDs. In the Philippines:
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a group of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels usually caused by fatty deposits that build up and block arteries and result in an increased risk of blood clots. In other cases, they are caused by damage in the arteries of organs like the brain, heart, kidneys and eyes. CVDs are the #1 cause of death in the Philippines and in the rest of the world. Examples of CVDs include:
- Ischaemic or coronary heart disease – narrowing of the blood vessels that supply the heart, often leading to heart attacks
- Cerebrovascular diseases – disorders affecting blood flow to the brain, like stroke
- Rheumatic heart disease – damage to the heart valves caused by rheumatic fever, often following untreated infections
- Congenital heart disease – structural heart defects present at birth
- Peripheral artery disease – reduced blood flow to limbs due to narrowed arteries
Cancers are a group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body. These cells can invade nearby tissues and, in more severe cases, spread to other parts of the body. It can be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and unhealthy lifestyle factors. Over 30% of cancers are preventable. Cancers are also curable when detected early through screening and treatment. The top 5 most frequent cancers among Filipinos include:
- Breast – Most prevalent in women (33,079 new cases, 2022)
- Lung – Most prevalent in men (23,728 new cases, 2022)
- Colorectum – (20,736 new cases, 2022)
- Liver – (12,544 new cases, 2022)
- Prostate – (9764 new cases, 2022)
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition in which the body is unable to properly regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels. It occurs either because the pancreas does not produce enough insulin (a hormone that helps glucose enter cells for energy), or because the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. If not managed properly, diabetes can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, blindness, and nerve damage. The three main types of diabetes are:
- Type 1 Diabetes – An autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells. It usually develops in childhood or adolescence.
- Type 2 Diabetes – The most common type, often linked to lifestyle factors such as being overweight, physical inactivity, and poor diet. The body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough.
- Gestational Diabetes – Occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth, but increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Chronic respiratory diseases (CRDs) are long-term conditions that affect the airways and other structures of the lungs, making it difficult for a person to breathe normally. These diseases are typically progressive, not fully curable, and often require ongoing management. Common types of CRDs include:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) – a group of lung diseases (like emphysema and chronic bronchitis) that block airflow and make breathing difficult.
- Asthma – a condition where the airways become inflamed and narrow, often triggered by allergens or irritants.
- Pulmonary fibrosis – scarring of lung tissue that leads to stiff lungs and breathing difficulties.
- Occupational lung diseases – caused by prolonged exposure to harmful substances at work, such as dust, chemicals, or fumes.
Mental health is a person’s emotional, psychological, and social well-being.
Mental health conditions are conditions that affect a person’s thinking, emotions, mood, behavior, or ability to relate to others and function in daily life and can range in severity and may be temporary or long-term. They can be caused by a combination of genetic, psychological, social, and environmental factors. They include depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) among others, that often require professional care such as counseling, therapy, medication, or a combination of these.
Neurological disorders are diseases of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves that can affect movement, communication, cognition, and body functions. These are medical conditions often caused by structural, biochemical, or electrical abnormalities in the nervous system. Examples of neurological disorders include epilepsy, dementia, and Parkinson’s disease that are typically managed with neurological care, including medication, rehabilitation, and support services.
Apart from the top five, there are hundreds of other conditions under the scope of NCDs that need to be equally addressed by the government through investing in preventive interventions and enhancing accessibility of health care services and treatment for Filipinos. Among others:
Obesity is a form of malnutrition–overnutrion–characterized by excessive fat deposits in the body. It is commonly measured using the Body Mass Index (BMI), which is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared (kg/m²). According to the World Health Organization (WHO):
- Overweight = BMI of 25.0 to 29.9
- Obese = BMI of 30.0 or higher
The 2023 National Nutrition Survey (NNS) of DOST-FNRI showed that 57.1% of adult Filipinos ages 20-59 are either overweight or obese, much higher compared to 40.2% or 4 in 10 adults in 2021.
- Where 17.3% or 1 in every 5 are overweight, while 39.8% or 2 in every 5 are obese among adults
- Among children ages 5-10, 12.9% were overweight and obese in 2023, versus 14% in 2021
- Among adolescents ages 10-19, 12.5% were overweight and obese in 2023 versus 13% in 2021
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a long-term condition where the kidneys gradually lose their ability to function properly over time. When kidney function to filter waste and excess fluids declines, waste builds up in the body, leading to serious health problems. Top common causes of CKD are diabetes and hypertension. CKD has no signs or symptoms thus, when detected is at a severe stage. CKD can lead to end-stage kidney or renal disease requiring dialysis or kidney transplant.
The Philippine Society of Nephrology estimates kidney disease to affect 7 million Filipinos in 2021, but may be underestimated. The National Kidney Transplant Institute estimates 1 Filipino every hour is diagnosed with kidney disease. A study published in 2023 revealed that the prevalence of CKD in the Philippines is at 35.94% which means 3 in every 10 Filipinos are suffering from the disease.
Eye health conditions refer to a range of diseases and disorders that affect the function, structure, or clarity of the eyes and vision. These conditions can be mild or serious, temporary or permanent, and may affect one or both eyes. Maintaining good eye health is essential for daily functioning, learning, and overall quality of life. Some include refractive errors like astigmatism, cataracts, glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy caused by complications of diabetes that damage the blood vessels in the retina.
Oral health conditions refer to diseases and disorders that affect the mouth, teeth, gums, tongue, and related structures. Smoking and a diet with too much sugary food without proper oral hygiene contributes to poor oral health. Common oral health conditions include dental caries (tooth decay), periodontal disease (gum disease) like gingivitis, oral cancer, tooth loss (Edentulism) and birth defects like cleft lip and palate.
Thyroid conditions are disorders that affect the thyroid gland, a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck. The thyroid produces hormones that regulate the body’s metabolism, which influences energy levels, heart rate, temperature, and how the body uses food. Common thyroid conditions include hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), goiter, thyroid nodules or lumps within the thyroid, and thyroid cancer.
Autoimmune diseases are conditions in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy cells, tissues, or organs when normally, the immune system should defend the body against harmful invaders like viruses and bacteria. In autoimmune diseases, however, the immune response becomes overactive or misdirected, causing inflammation and damage to the body’s own systems. Some common autoimmune diseases include:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis – Affects joints, causing pain and swelling
- Lupus (SLE) – Affects multiple organs including skin, joints, and kidneys
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) – Damages the protective covering of nerves
- Psoriasis – Leads to skin cell buildup and inflammation
Sources : World Health Organization & NCD Alliance
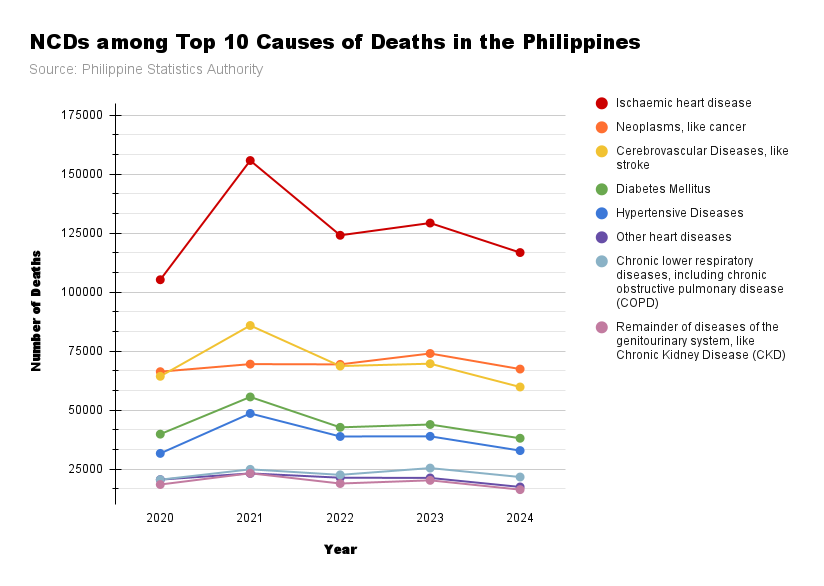
| NCDs among Top 10 Causes of Deaths | Number of Deaths by Year | ||||
| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| Ischaemic heart disease | 105281 | 155775 | 124110 | 129300 | 116,795 |
| Neoplasms, like cancer | 66342 | 69541 | 69433 | 74042 | 67,449 |
| Cerebrovascular Diseases, like stroke | 64381 | 85904 | 68726 | 69722 | 59,858 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 39884 | 55636 | 42766 | 43964 | 38,138 |
| Hypertensive Diseases | 31727 | 48647 | 38897 | 38962 | 32,916 |
| Other heart diseases | 20617 | 23253 | 21433 | 21337 | 17,518 |
| Chronic lower respiratory diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) | 20599 | 24976 | 22645 | 25512 | 21,724 |
| Remainder of diseases of the genitourinary system, like Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) | 18545 | 23309 | 18969 | 20320 | 16,377 |
| Source : Philippine Statistics Authority | |||||
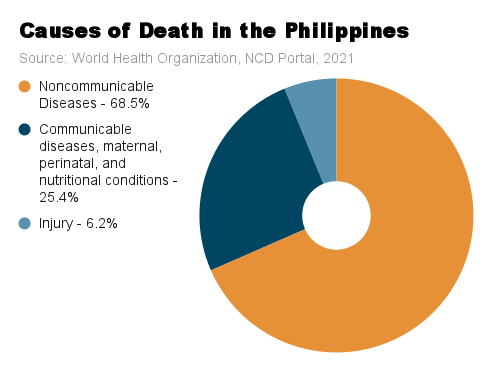
| Cause of Death | % (some figures rounded off) | Number of Deaths | |
| Noncommunicable Diseases (NCDs) | 68.5% | 622, 232 | |
| Cardiovascular Diseases | 34% | 304,588 | |
| Cancer | 11% | 98,192 | |
| Chronic Respiratory Diseases | 5% | 43,026 | |
| Diabetes | 4% | 34, 747 | |
| Other NCDs | 16% | 141,679 | |
| Communicable Diseases, Maternal, Perinatal, Nutritional conditions | 25.4% | ||
| Injuries | 6.2% | ||
| Source: World Health Organization, 2021 https://data.who.int/countries/608; https://ncdportal.org/CountryProfile/GHE110/PHL#mor1 | |||
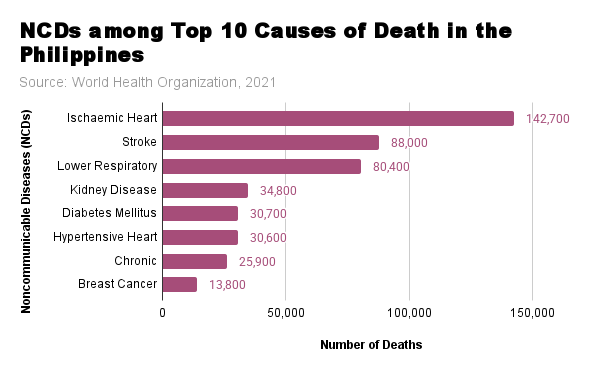
| NCDs among Top 10 causes of Death in the Philippines | Number of Deaths (figures rounded off) |
| Ischaemic Heart Disease | 142,700 |
| Stroke | 88,000 |
| Lower Respiratory Infections | 80,400 |
| Kidney Disease | 34,800 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 30,700 |
| Hypertensive Heart Disease | 30,600 |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | 25,900 |
| Breast Cancer | 13,800 |
| Source: World Health Organization, 2021 https://data.who.int/countries/608 | |